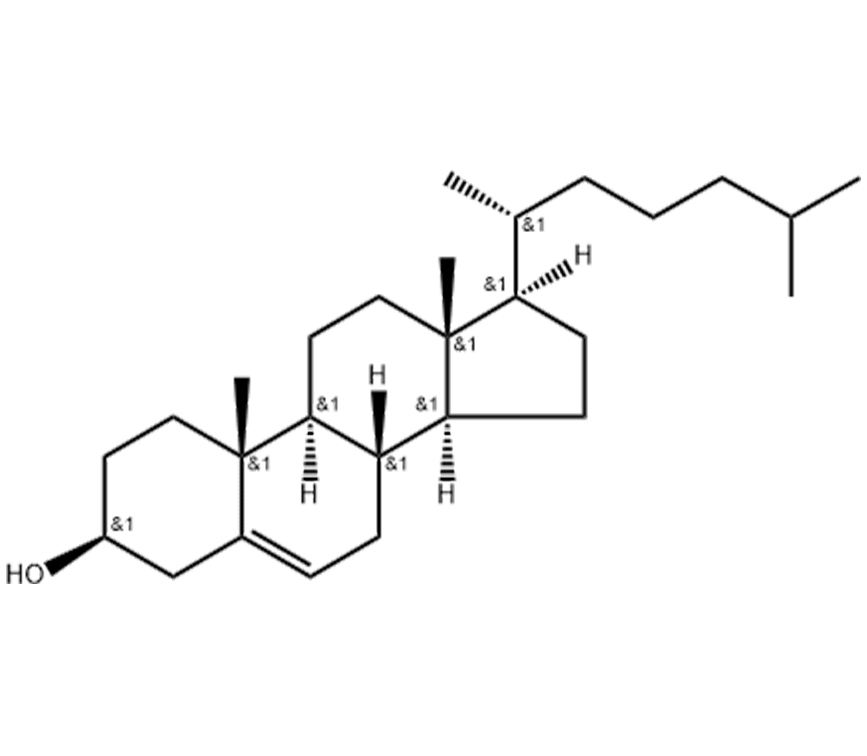
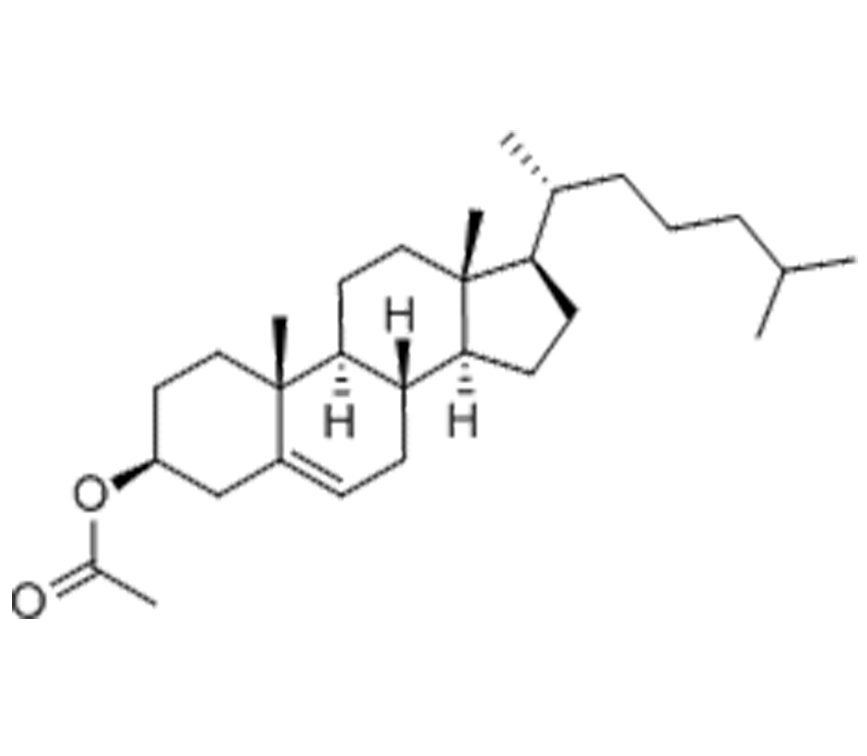
Was ist Cholesterin auf pflanzlicher Basis?
Pflanzliches Cholesterin (Phytosterine): ein natürlich vorkommender "Gesundheitsregulator".
Pflanzliches Cholesterin, dessen Hauptbestandteil Phytosterine sind, ist eine Klasse von natürlich vorkommenden Wirkstoffen, die in Pflanzen weit verbreitet sind. Im Vergleich zu Cholesterin tierischer Herkunft (wie es in Fleisch und Milchprodukten vorkommt) haben beide zwar eine ähnliche chemische Struktur (beide enthalten einen Steroidring), aber Phytosterine besitzen eine spezifische zusätzliche Seitenkette, die zu einer einzigartigen physiologischen Aktivität und einem höheren Sicherheitsprofil führt, was sie zu einem natürlich "gesundheitsfreundlichen" Inhaltsstoff macht.
Zentrale Merkmale: Natürliche Vorteile in Struktur und Funktion
Struktureller Unterschied: Im Vergleich zu Cholesterin tierischen Ursprungs haben Phytosterine eine zusätzliche Seitenkette in ihrer Molekularstruktur. Dieser Unterschied ermöglicht es ihnen, eine einzigartige Rolle im menschlichen Körper zu spielen, indem sie mit Cholesterin im Darm konkurrieren, die Cholesterinabsorption durch den Körper verringern und so zur Regulierung des Low-Density-Lipoprotein-Cholesterinspiegels (LDL-C) im Blut beitragen.
Natürlich weithin verfügbar: Phytosterine sind in Nüssen (z. B. Walnüssen und Mandeln), Samen (z. B. Leinsamen und Sonnenblumenkernen), Hülsenfrüchten, Vollkorngetreide und Pflanzenölen (z. B. Soja- und Maisöl) enthalten und fungieren als "natürliche Schutzschicht", die von den Pflanzen selbst synthetisiert wird.
Gesundheitlicher Nutzen: Wissenschaftlich erwiesener Schutz des Herz-Kreislauf-Systems
Mehrere Studien haben die positiven Auswirkungen einer angemessenen Zufuhr von Pflanzensterinen auf die menschliche Gesundheit bestätigt:
1. Ihre Hauptfunktion besteht darin, die Cholesterinabsorption im Darm zu hemmen und so den Blutspiegel des "schlechten" Cholesterins (LDL-C) zu senken, wodurch das Risiko von Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen verringert wird.
2. In Verbindung mit einer gesunden Ernährung und Lebensweise können sie als "natürlicher Kofaktor" für das kardiovaskuläre Gesundheitsmanagement dienen. Sie belasten den Stoffwechsel nicht so stark wie tierisches Cholesterin und sind für einen langfristigen Verzehr geeignet.
Anwendungsszenarien: Von natürlichen Inhaltsstoffen zu funktionellen Produkten
1. Tägliche Nahrungsquellen: Sie kommen natürlich in einer Vielzahl von pflanzlichen Lebensmitteln vor und sind ein wesentlicher Bestandteil einer ausgewogenen Ernährung.
2. funktionelle Lebensmittelzusatzstoffe: Aufgrund ihrer nachgewiesenen gesundheitlichen Vorteile werden sie in der Lebensmittelindustrie in großem Umfang eingesetzt - beispielsweise in Produkten wie Margarine, Joghurt und funktionellen Getränken - und ermöglichen es den Verbrauchern, ihre tägliche Ernährung auf einfache Weise zu ergänzen und die gesundheitlichen Vorteile dieser Produkte zu verbessern.
Als natürlich vorkommende Wirkstoffe sind Pflanzensterine mit ihrem Hauptwert "Cholesterinregulierung und Schutz des Herz-Kreislauf-Systems" in der täglichen Ernährung enthalten und durch industrielle Anwendungen wichtige Bestandteile von funktionellen Produkten. Sie dienen als wertvolle Brücke zwischen natürlichen Pflanzen und der menschlichen Gesundheit.
Pflanzliches Cholesterin, dessen Hauptbestandteil Phytosterine sind, ist eine Klasse von natürlich vorkommenden Wirkstoffen, die in Pflanzen weit verbreitet sind. Im Vergleich zu Cholesterin tierischer Herkunft (wie es in Fleisch und Milchprodukten vorkommt) haben beide zwar eine ähnliche chemische Struktur (beide enthalten einen Steroidring), aber Phytosterine besitzen eine spezifische zusätzliche Seitenkette, die zu einer einzigartigen physiologischen Aktivität und einem höheren Sicherheitsprofil führt, was sie zu einem natürlich "gesundheitsfreundlichen" Inhaltsstoff macht.
Zentrale Merkmale: Natürliche Vorteile in Struktur und Funktion
Struktureller Unterschied: Im Vergleich zu Cholesterin tierischen Ursprungs haben Phytosterine eine zusätzliche Seitenkette in ihrer Molekularstruktur. Dieser Unterschied ermöglicht es ihnen, eine einzigartige Rolle im menschlichen Körper zu spielen, indem sie mit Cholesterin im Darm konkurrieren, die Cholesterinabsorption durch den Körper verringern und so zur Regulierung des Low-Density-Lipoprotein-Cholesterinspiegels (LDL-C) im Blut beitragen.
Natürlich weithin verfügbar: Phytosterine sind in Nüssen (z. B. Walnüssen und Mandeln), Samen (z. B. Leinsamen und Sonnenblumenkernen), Hülsenfrüchten, Vollkorngetreide und Pflanzenölen (z. B. Soja- und Maisöl) enthalten und fungieren als "natürliche Schutzschicht", die von den Pflanzen selbst synthetisiert wird.
Gesundheitlicher Nutzen: Wissenschaftlich erwiesener Schutz des Herz-Kreislauf-Systems
Mehrere Studien haben die positiven Auswirkungen einer angemessenen Zufuhr von Pflanzensterinen auf die menschliche Gesundheit bestätigt:
1. Ihre Hauptfunktion besteht darin, die Cholesterinabsorption im Darm zu hemmen und so den Blutspiegel des "schlechten" Cholesterins (LDL-C) zu senken, wodurch das Risiko von Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen verringert wird.
2. In Verbindung mit einer gesunden Ernährung und Lebensweise können sie als "natürlicher Kofaktor" für das kardiovaskuläre Gesundheitsmanagement dienen. Sie belasten den Stoffwechsel nicht so stark wie tierisches Cholesterin und sind für einen langfristigen Verzehr geeignet.
Anwendungsszenarien: Von natürlichen Inhaltsstoffen zu funktionellen Produkten
1. Tägliche Nahrungsquellen: Sie kommen natürlich in einer Vielzahl von pflanzlichen Lebensmitteln vor und sind ein wesentlicher Bestandteil einer ausgewogenen Ernährung.
2. funktionelle Lebensmittelzusatzstoffe: Aufgrund ihrer nachgewiesenen gesundheitlichen Vorteile werden sie in der Lebensmittelindustrie in großem Umfang eingesetzt - beispielsweise in Produkten wie Margarine, Joghurt und funktionellen Getränken - und ermöglichen es den Verbrauchern, ihre tägliche Ernährung auf einfache Weise zu ergänzen und die gesundheitlichen Vorteile dieser Produkte zu verbessern.
Als natürlich vorkommende Wirkstoffe sind Pflanzensterine mit ihrem Hauptwert "Cholesterinregulierung und Schutz des Herz-Kreislauf-Systems" in der täglichen Ernährung enthalten und durch industrielle Anwendungen wichtige Bestandteile von funktionellen Produkten. Sie dienen als wertvolle Brücke zwischen natürlichen Pflanzen und der menschlichen Gesundheit.